上海金畔生物科技有限公司为生命科学和医药研发人员提供生物活性分子抑制剂、激动剂、特异性抑制剂、化合物库、重组蛋白,专注于信号通路和疾病研究领域。
Reveromycin A (Synonyms: 雷弗霉素A)
Reveromycin A 是一种从链霉菌属中分离出来的苯甲醌类抗生素 (antibiotic),是选择性的真核细胞中蛋白质合成 (protein synthesis) 抑制剂。Reveromycin A 通过诱导破骨细胞的凋亡 (apoptosis) 来抑制骨吸收。Reveromycin A 对肿瘤细胞系具有抗增殖活性,并具有抗真菌 (antifungal) 活性。
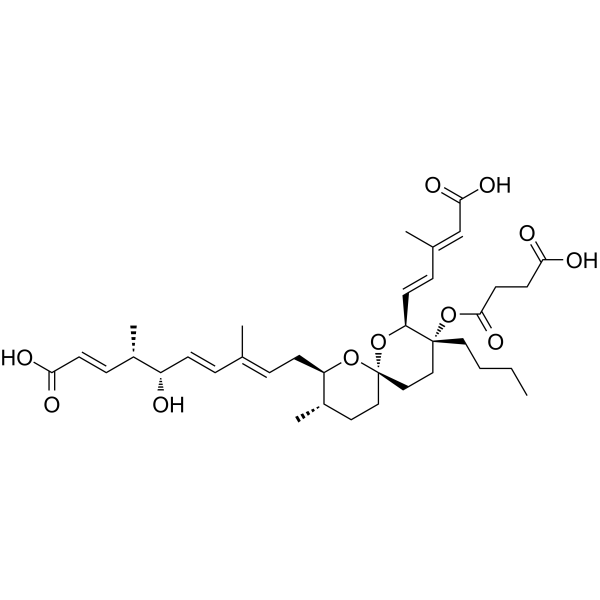
Reveromycin A Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 134615-37-5
| 规格 | 是否有货 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | 询价 | ||
| 5 mg | 询价 | ||
| 10 mg | 询价 | ||
| 25 mg | 询价 |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
| 生物活性 |
Reveromycin A, a benzoquinoid antibiotic isolated from the genus Streptomyces, is a selective inhibitor of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Reveromycin A inhibits bone resorption by inducing apoptosis specifically in osteoclasts. Reveromycin A has antiproliferative activity against tumor cell lines and antifungal activity[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Reveromycin A inhibits protein synthesis in osteoclasts (OCs) by selectively blocking enzymatic activity of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase[2]. Shanghai Jinpan Biotech Co Ltd has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Reveromycin A (20 mg/kg; twice daily; i.v.; for 3 days) significantly decreases numbers of OCs without affecting numbers of osteoblasts in normal 4-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats[2]. Shanghai Jinpan Biotech Co Ltd has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 分子量 |
660.79 |
| Formula |
C36H52O11 |
| CAS 号 |
134615-37-5 |
| 中文名称 |
雷弗霉素A |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
| 储存方式 |
Please store the product under the recommended conditions in the Certificate of Analysis. |
| 参考文献 |
|
所有产品仅用作科学研究或药证申报,我们不为任何个人用途提供产品和服务
