上海金畔生物科技有限公司为生命科学和医药研发人员提供生物活性分子抑制剂、激动剂、特异性抑制剂、化合物库、重组蛋白,专注于信号通路和疾病研究领域。
α-Lipoic Acid (Synonyms: α-硫辛酸; Thioctic acid; (±)-α-Lipoic acid; DL-α-Lipoic acid) 纯度: 98.03%
α-Lipoic Acid 是一种抗氧化剂,是线粒体酶复合物的重要辅助因子。α-Lipoic Acid 可抑制 NF-κB 依赖性的 HIV-1 LTR 活化。α-Lipoic Acid 诱导内质网应激 (ER) 介导的肝癌细胞凋亡 (apoptosis)。
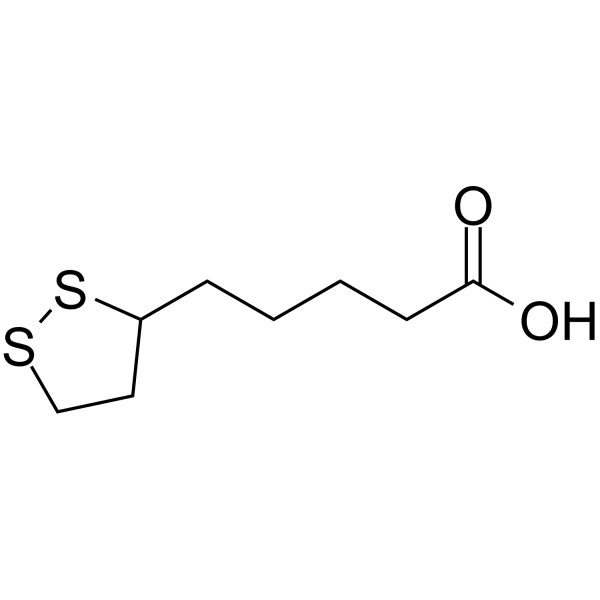
α-Lipoic Acid Chemical Structure
CAS No. : 1077-28-7
| 规格 | 价格 | 是否有货 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO | ¥550 | In-stock | |
| 500 mg | ¥500 | In-stock | |
| 1 g | 询价 | ||
| 5 g | 询价 |
* Please select Quantity before adding items.
α-Lipoic Acid 相关产品
•相关化合物库:
- Natural Product Library Plus
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Plus
- FDA-Approved Drug Library Mini
- Bioactive Compound Library Plus
- Anti-Infection Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Metabolism/Protease Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Product Library
- FDA-Approved Drug Library
- Anti-Cancer Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Drug Repurposing Compound Library
- Antioxidants Compound Library
- Differentiation Inducing Compound Library
- Lipid Compound Library
- Oxygen Sensing Compound Library
- NMPA-Approved Drug Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- FDA Approved & Pharmacopeial Drug Library
- Anti-Breast Cancer Compound Library
- Anti-Pancreatic Cancer Compound Library
- Anti-Blood Cancer Compound Library
- Anti-Cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Obesity Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound Library
- Transcription Factor Targeted Library
- Glucose Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Liver Cancer Compound Library
| 生物活性 |
α-Lipoic Acid is an antioxidant, which is an essential cofactor of mitochondrial enzyme complexes. α-Lipoic Acid inhibits NF-κB-dependent HIV-1 LTR activation[1][2][3]. α-Lipoic Acid induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptosis in hepatoma cells[4]. |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 & Target[1][2] |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
The long terminal repeat (LTR) of HIV-1 is the target of cellular transcription factors such as NF-κB, and serves as the promoter-enhancer for the viral genome when integrated in host DNA[1]. α-Lipoic Acid (Alpha-Lipoic acid, ALA), a naturally occurring dithiol compound, plays an essential role in mitochondrial bioenergetics. α-Lipoic Acid reduces lipid accumulation in the liver by regulating the transcriptional factors SREBP-1, FoxO1, and Nrf2, and their downstream lipogenic targets via the activation of the SIRT1/LKB1/AMPK pathway. Treatment of cells with α-Lipoic Acid (250, 500 and 1000 μM) significantly increases the NAD+/NADH ratio in HepG2 cells (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Treatment with α-Lipoic Acid (50, 125, 250 and 500 μM) increases SIRT1 activity in HepG2 cells. α-Lipoic Acid (50, 125, 250, 500 and 1000 μM) increases phosphorylation of AMPK and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) in HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent fashion[1]. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
C57BL/6J mice, divided into four groups, are fed an high-fat diet (HFD) for 24 weeks to induce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) followed by daily administration of α-Lipoic Acid. Then, the effects of α-Lipoic Acid on hepatic lipid accumulation in long-term HFD-fed mice are assessed. Administration of α-Lipoic Acid (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg) markedly reduces visceral fat mass in mice. In addition, α-Lipoic Acid (100 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg) treatment inhibits the appetite and causes a dramatic weight loss (all P<0.05)[1]. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||
| Clinical Trial |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 分子量 |
206.33 |
||||||||||||||||
| Formula |
C8H14O2S2 |
||||||||||||||||
| CAS 号 |
1077-28-7 |
||||||||||||||||
| 中文名称 |
α-硫辛酸 |
||||||||||||||||
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
||||||||||||||||
| 储存方式 |
|
||||||||||||||||
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (484.66 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) * “≥” means soluble, but saturation unknown. 配制储备液
*
请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 In Vivo:
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解方案。以下溶解方案都请先按照 In Vitro 方式配制澄清的储备液,再依次添加助溶剂: ——为保证实验结果的可靠性,澄清的储备液可以根据储存条件,适当保存;体内实验的工作液,建议您现用现配,当天使用; 以下溶剂前显示的百
|
||||||||||||||||
| 参考文献 |
|
| Cell Assay [1] |
The human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line is cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37°C and 5% CO2. HepG2 cells are treated with AMPK inhibitor (CC, 20 μM, 0.5 h), SIRT1 inhibitor (NA, 10 mM, 12 or 24 h), and AMPK activator (AICAR, 2 mM, 1 h), Palmitate (PA, 125 μM, 12 h) and α-Lipoic Acid (250 μM, 6 or 12 h)[1]. 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
|---|---|
| Animal Administration [1] |
Mice[1] 上海金畔生物科技有限公司 has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
| 参考文献 |
|
所有产品仅用作科学研究或药证申报,我们不为任何个人用途提供产品和服务
